Everything You Need to Understand About Geotechnical Engineering for Your Following Job
Everything You Need to Understand About Geotechnical Engineering for Your Following Job
Blog Article
Exploring the Interdisciplinary Nature of Geotechnical Design and Its Influence on Ground Improvement and Foundation Layout
The interdisciplinary nature of geotechnical design plays a critical role fit cutting-edge ground renovation strategies and structure design methodologies. By integrating understandings from architectural, ecological, and geological self-controls, geotechnical engineers are geared up to attend to complicated dirt habits and site-specific difficulties. This collaborative strategy not just boosts the efficiency of techniques such as dirt stabilization and dynamic compaction yet additionally makes certain that tasks abide by sustainability concepts. What ramifications does this interdisciplinary synergy have for future developments in the field, particularly in the context of emerging building technologies?
Overview of Geotechnical Design
Geotechnical engineering is a critical branch of civil design that focuses on the actions of earth materials and their interaction with frameworks. This self-control encompasses the research study of groundwater, rock, and soil, aiming to comprehend their residential or commercial properties and how they affect the performance of civil engineering tasks. Geotechnical engineers evaluate the hydraulic and mechanical behavior of these materials to make certain the security and security of structures such as structures, bridges, and preserving wall surfaces.
The scope of geotechnical design includes website examinations, soil sampling, and screening, in addition to analysis of dirt mechanics and rock mechanics. Engineers use sophisticated strategies to evaluate ground problems, recognize possible threats, and layout effective ground enhancement services. This may include techniques such as dirt stabilization, grouting, and making use of geosynthetics, which boost the strength and durability of the ground.
Moreover, geotechnical design plays a crucial function in foundation design, determining proper structure types based on soil qualities and packing problems. By integrating strenuous testing and analysis, geotechnical designers add significantly to the sustainability and durability of facilities, guaranteeing that structures can endure functional and environmental stresses gradually.
Trick Interdisciplinary Relationships

In addition, environmental engineering plays an essential function in examining the impact of geotechnical tasks on the surrounding ecosystem. This collaboration is essential for establishing lasting techniques that reduce ecological degradation during excavation or ground renovation processes.
In addition, the combination of geotechnical design with geology boosts the understanding of subsurface problems, helping with even more accurate site characterizations (all about geotechnical engineering). This connection help in risk evaluation, especially in areas susceptible to landslides or seismic activity, thus informing danger mitigation strategies
Last but not least, innovations in technology have caused interdisciplinary cooperation with information scientific research and geoinformatics. These areas add to improved modeling and evaluation techniques, enabling for extra specific predictions of dirt behavior under various problems. Therefore, the interconnectedness of these self-controls enhances geotechnical engineering, promoting innovation and effectiveness in foundation design and ground renovation.
Ground Improvement Techniques
Ground enhancement techniques are vital methods employed to improve the design homes of dirt, consequently boosting its load-bearing capacity and security. These methods are particularly important in locations where all-natural soil problems are poor for sustaining structural tons or where ecological factors may jeopardize dirt honesty.
Commonalities improvement methods include dirt compaction, which boosts density and minimizes void spaces, and grouting, which includes infusing products into soil to load voids and bind particles with each other - geotechnical specialist. Other strategies include the setup of dirt nails and supports, which supply added assistance, and the use of geosynthetics to enhance soil structures. Deep blending approaches, such as soil-cement columns, can additionally significantly improve the stamina and rigidity of weak dirts
Additionally, dynamic compaction and vibro-replacement strategies are usually used to enhance dirt buildings sitting. These techniques can mitigate problems associated with negotiation and liquefaction, especially in seismic locations. By using a mix of these ingenious methods, geotechnical designers can properly address site-specific challenges, making sure that the structure systems will carry out properly under prepared for loading conditions, hence adding to total project success.
Foundation Design Considerations
Efficient foundation design considerations are critical for the long life and stability of frameworks. A well-designed foundation needs to appropriately support the lots of the building while fitting dirt conditions, environmental elements, and potential adjustments gradually. Trick aspects include dirt bearing ability, negotiation characteristics, and groundwater problems.
Understanding the dirt profile through geotechnical investigations is important, as it educates the choice of structure type-- be it shallow, deep, or specialized methods such as heap structures or floor covering foundations. The anticipated lots, including online, dead, and environmental tons, must be accurately calculated to ensure the foundation can withstand possible failing devices, such as moving, reversing, or excessive negotiation.
Furthermore, considerations for frost deepness, seismic activity, and prospective soil liquefaction in seismic zones are essential. Additionally, drainage and dampness control have to be integrated right into the structure layout to minimize problems associated to hydrostatic pressure and dirt disintegration.
Cooperation among designers, designers, and geotechnical professionals is important to develop a comprehensive foundation design that not only fulfills regulatory needs yet also makes sure the lasting performance and safety of the framework. Ultimately, complete planning and cutting-edge solutions are required to attend to the intricacies intrinsic in foundation layout.
Study and Best Practices
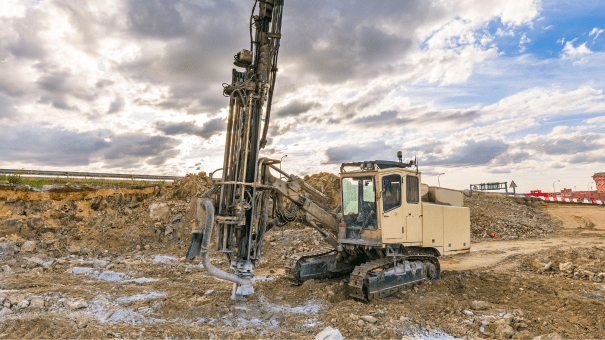
One notable instance research entails the usage of see here now deep soil mixing in a skyscraper task in a seismic zone. This strategy substantially enhanced the dirt's toughness and security, permitting a much safer and more reliable structure system (about geotechnical engineering). The task highlighted the significance of choosing proper ground enhancement techniques based upon site-specific problems, including dirt type and loading demands
An additional example is the application of dynamic compaction for enhancing the news bearing capacity of weak soils below an industrial facility. This method efficiently minimized settlement concerns and improved general site performance, showing the efficiency of combining typical design methods with modern-day innovation.
Best practices acquired from these study emphasize the need of extensive website examinations, cooperation among multidisciplinary groups, and the unification of innovative modeling devices. By embracing these lessons, geotechnical designers can optimize foundation designs and ground enhancement strategies, eventually resulting in more secure and more sustainable building and construction outcomes.
Final Thought
In final thought, the interdisciplinary nature of geotechnical design dramatically boosts ground renovation and structure style. By integrating concepts from various design disciplines, customized methods are developed to deal with particular obstacles connected to dirt homes and environmental impacts. This collective method not only ensures ideal structure stability and safety and security however additionally advertises lasting construction practices. Proceeded expedition of these interdisciplinary More Info relationships will even more progress the field, resulting in cutting-edge solutions that react properly to advancing design demands.
The scope of geotechnical engineering includes site examinations, soil sampling, and screening, as well as analysis of soil technicians and rock mechanics. The relationship in between geotechnical design and structural engineering is particularly essential, as the efficiency of structures is heavily affected by dirt habits and properties.Typical ground improvement methods include soil compaction, which enhances density and lowers void areas, and grouting, which entails injecting products into soil to fill voids and bind fragments together. Various other techniques include the setup of soil nails and supports, which supply added assistance, and the usage of geosynthetics to reinforce dirt structures. A well-designed foundation has to sufficiently sustain the load of the building while suiting dirt problems, environmental variables, and potential modifications over time.
Report this page